Strong and dangerous M6.3 earthquake struck Veracruz, Mexico
A strong earthquake measuring M6.3 on the Richter scale was registered in Veracruz, Mexico, on July 29, 2014, at 10:46 UTC. USGS reported depth of 95.1 km (59.1 miles), EMSC is reporting M6.4 at depth of 100 km (preliminary data).
Epicenter was located 19 km (12 miles) SW of Juan Rodriguez Clara (population 12 332), 60 km (37 miles) W of Sayula de Aleman, 65 km (40 miles) W of Acayucan and 418 km (260 miles) ESE of capital Mexico City.
There are 1 677 577 people living within 100 km radius.
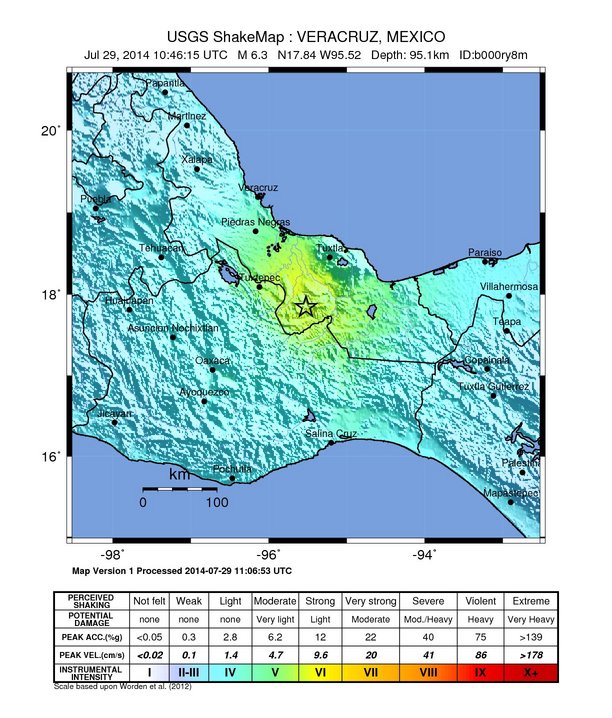
USGS issued yellow alert for shaking-related fatalities. Some casualties are possible and the impact should be relatively localized. Past events with this alert level have required a local or regional level response.
Green alert was issued for economic losses. There is a low likelihood of damage.
Overall, the population in this region resides in structures that are a mix of vulnerable and earthquake resistant construction. Recent earthquakes in this area have caused secondary hazards such as landslides that might have contributed to losses.
Population exposure
Population per ˜1 sq. km. from LandScan
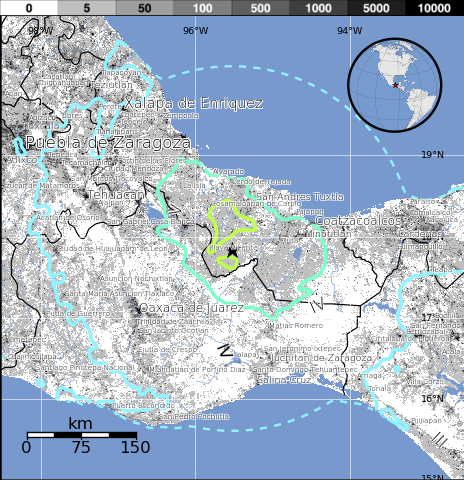
Selected cities exposed
from GeoNames Database of Cities with 1,000 or more residents
| MMI | City | Population |
|---|---|---|
| VI | Villa Azueta | 7k |
| VI | Otatitlan | 5k |
| VI | Playa Vicente | 8k |
| VI | Carlos A. Carrillo | 18k |
| VI | Cosamaloapan de Carpio | 29k |
| V | Corral Nuevo | 5k |
| IV | Oaxaca de Juarez | 263k |
| IV | Villahermosa | 362k |
| IV | Xalapa de Enriquez | 425k |
| IV | Tuxtla Gutierrez | 481k |
| IV | Puebla de Zaragoza | 1,590k |
(k = x1,000)
Seismotectonics of Mexico
Located atop three of the large tectonic plates, Mexico is one of the world's most seismically active regions. The relative motion of these crustal plates causes frequent earthquakes and occasional volcanic eruptions. Most of the Mexican landmass is on the westward moving North American plate. The Pacific Ocean floor south of Mexico is being carried northeastward by the underlying Cocos plate. Because oceanic crust is relatively dense, when the Pacific Ocean floor encounters the lighter continental crust of the Mexican landmass, the ocean floor is subducted beneath the North American plate creating the deep Middle American trench along Mexico's southern coast. Also as a result of this convergence, the westward moving Mexico landmass is slowed and crumpled creating the mountain ranges of southern Mexico and earthquakes near Mexico's southern coast. As the oceanic crust is pulled downward, it melts; the molten material is then forced upward through weaknesses in the overlying continental crust. This process has created a region of volcanoes across south-central Mexico known as the Cordillera Neovolcánica.
The area west of the Gulf of California, including Mexico's Baja California Peninsula, is moving northwestward with the Pacific plate at about 50 mm per year. Here, the Pacific and North American plates grind past each other creating strike-slip faulting, the southern extension of California's San Andreas fault. In the past, this relative plate motion pulled Baja California away from the coast forming the Gulf of California and is the cause of earthquakes in the Gulf of California region today.
Mexico has a long history of destructive earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. In September 1985, a magnitude 8.1 earthquake killed more than 9,500 people in Mexico City. In southern Mexico, Volcán de Colima and El Chichón erupted in 2005 and 1982, respectively. Paricutín volcano, west of Mexico City, began venting smoke in a cornfield in 1943; a decade later this new volcano had grown to a height of 424 meters. Popocatépetl and Ixtaccíhuatl volcanos ("smoking mountain" and "white lady", respectively), southeast of Mexico City, occasionally vent gas that can be clearly seen from the City, a reminder that volcanic activity is ongoing. In 1994 and 2000 Popocatépetl renewed its activity forcing the evacuation of nearby towns, causing seismologists and government officials to be concerned about the effect a large-scale eruption might have on the heavily populated region. Popocatépetl volcano last erupted in 2010. (USGS) More information on regional seismicity and tectonics
Featured image: Google 2014 + EMSC

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.