Monster black hole lurking inside one of the tiniest galaxies ever known

A supermassive blackhole has been found inside the tiniest galaxy ever found, the M60-UCD1, located about 54 million light years away from Earth. Researchers used NASA’s Hubble and the Gemini North 8-meter optical and infrared telescope on Hawaii to observe and measure the black hole’s mass.
The black hole they found is five times the mass of the black hole at the center of our Milky Way. Yet is located inside a galaxy that crams 140 million stars within a diameter of about 300 light-years, only 1/500th of the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy.
One would get to see at least one million stars living in that galaxy with naked eyes when we can see only 4000 stars in ours from the surface of the earth. Apparently this is the densest galaxy ever seen. Their study suggests that there may be many compact galaxies in the universe with massive blackholes.
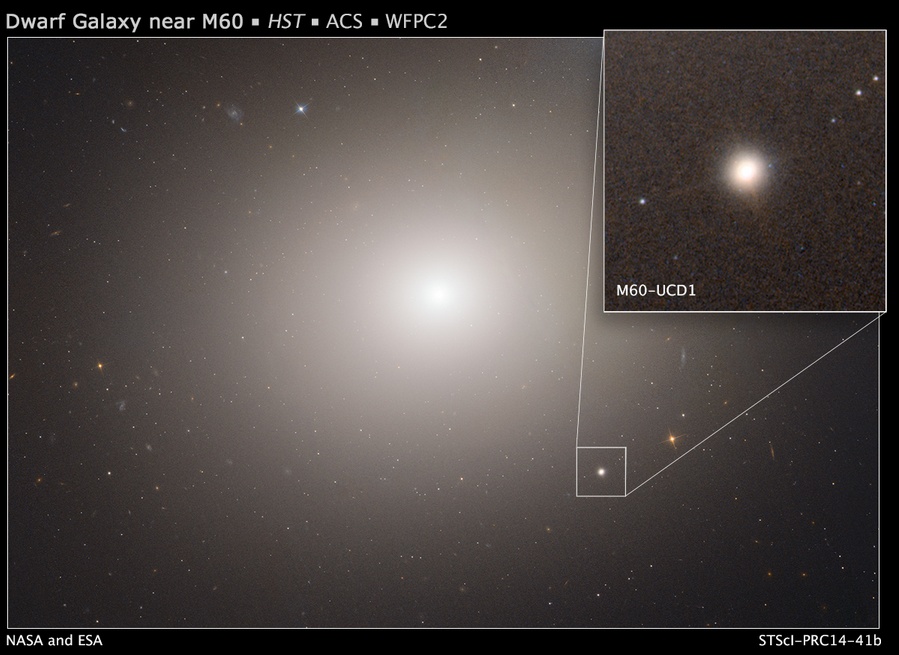

Image credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration
The observation also suggests dwarf galaxies may actually be the stripped remnants of larger galaxies that were torn apart during collisions with other galaxies rather than small islands of stars born in isolation. Findings of the study were published in the journal Nature on September 18. Astronomer Anil Chandra Seth of University of Utah was lead author of an international study of the dwarf galaxy.
"We don't know of any other way you could make a black hole so big in an object this small," Anil Chandra Seth says.
The black hole in the Milky Way has a mass of four million suns, making up less than 0.01% of the total mass of the galaxy. On the other hand, the super massive black hole at the center of M60-UCD1 is a surprising 15% of the galaxy’s total mass.
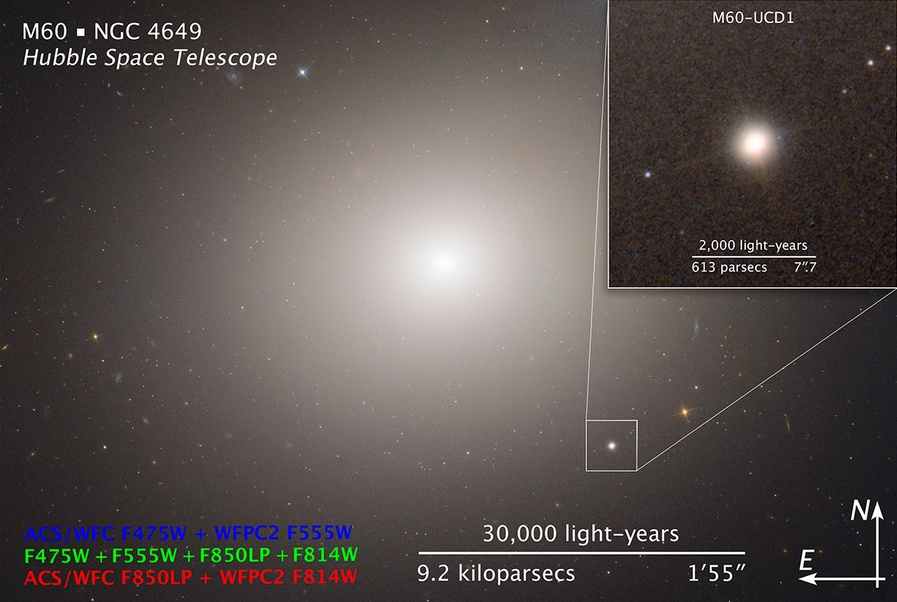
Compass and scale image for M60. Credit: NASA, ESA, and Z. Levay (STScI)
Seth explained the matter saying that that M60-UCD1 was possibly once a large galaxy with 10 billion stars, but then it passed very close to the center of an even larger galaxy, M60, and in that process all the stars and dark matter in the outer part of the galaxy were torn away and became part of M60.
M60 is said to have it's own massive black hole that weighs 4.5 billion solar masses, or more than 1 000 times bigger than the black hole in our galaxy. Calculations show both galaxies are 50 million light-years away.
Sources: NASA, Hubble Space Telescope
Featured image: Grand Design Spiral Galaxy M81. Credit: NASA, ESA, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.