Lava lake rises at Hawaii’s Kilauea volcano

The summit of Kīlauea volcano continues to inflate, and the summit lava lake rose to within about 2 meters (~7 feet) of the Overlook crater rim on Monday, April 27, 2015, according to Kilauea activity report issued by Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) yesterday. This is the highest the lava lake has reached during the current summit eruption.
Kīlauea's summit accumulated a total of about 7.5 microradians since inflation started on Tuesday, April 21, HVO's report continues.
Seismicity beneath the summit and the upper East Rift Zone is elevated.
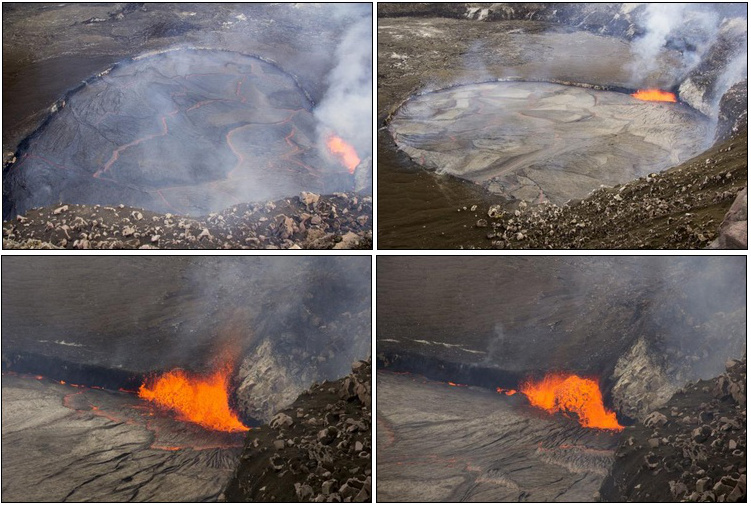

Top left: This photo shows the lava lake in the Overlook crater when it reached to within 3 m (10 ft) of the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu on April 26, 2015. Top right: This photo shows another view of the lava lake, from a different perspective, at the same time. Bottom left: This is a view of spattering at the east corner of the lava lake on April 26. Bottom right: Another view of spattering. Images credit: USGS/HVO.
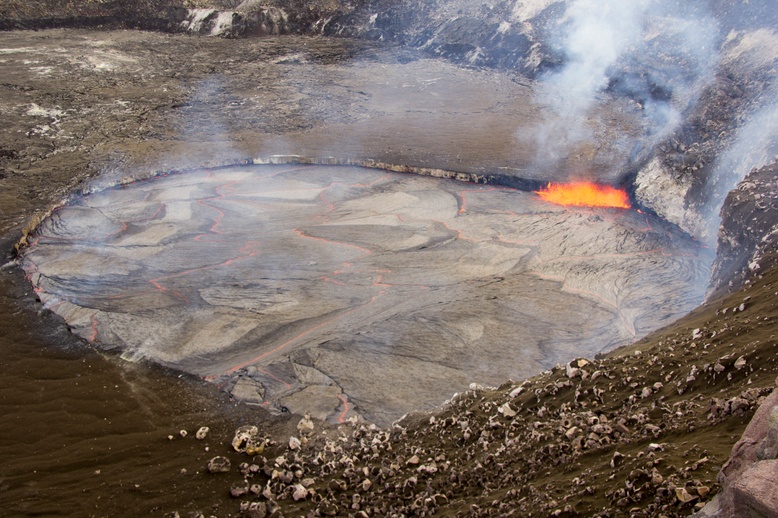

Lava lake in the Overlook crater on April 26, 2015 when it reached to within 3 m (10 ft) of the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu. Image credit: USGS/HVO
Sulfur dioxide emission rates averaged 3 000 – 5 200 tonnes/day for the week ending April 21.
Webcam views of flow field incandescence indicate that surface flows remain active northeast of Puʻu ʻŌʻō. The most distant activity was burning forest about 8 km (5 miles) northeast of the crater when mapped on April 23.
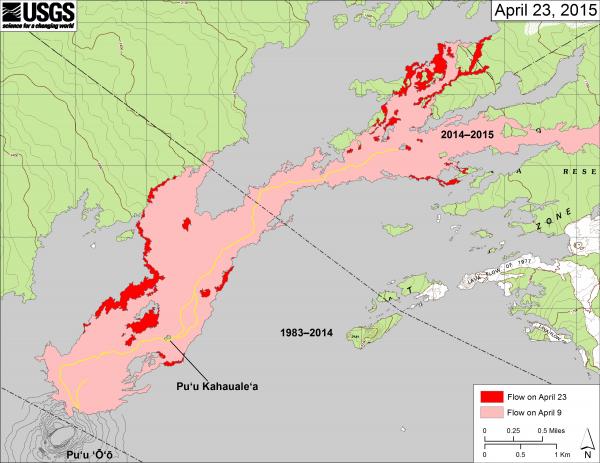
This map shows recent changes to Kīlauea’s active East Rift Zone lava flow field. The area of the flow on April 9 is shown in pink, while widening and advancement of the flow as of April 23 is shown in red. Puʻu ʻŌʻō lava flows erupted prior to June 27, 2014, are shown in gray. Image credit: USGS/HVO.
The summit lava lake is within an elliptical crater (unofficially called the Overlook crater), which has dimensions of approximately 160 m (520 ft) by 210 m (690 ft), inset within the eastern portion of Halemaʻumaʻu Crater. The lake level has varied from about 25 m to more than 200 m (out of sight) below the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu Crater. The Overlook crater has been more-or-less continuously active since it opened during a small explosive event on March 19, 2008. The lake level responds to summit tilt changes with the lake generally receding during deflation and rising during inflation.
Since 2013, the lava level has been typically between 30 m (100 ft) and 60 m (200 ft) below the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu Crater. Small collapses in the Overlook crater are common, and over time have resulted in a gradual enlargement of the Overlook crater. The ambient SO2 concentrations near the vent vary greatly, but are persistently higher than 10 ppm and frequently exceed 50 ppm (upper limit of detector) during moderate trade winds. The gas plume typically includes a small amount of ash-sized tephra (mostly fresh spatter bits and Pele's hair from the circulating lava lake). The heaviest pieces are deposited onto nearby surfaces while the finer bits can be carried several kilometers before dropping out of the plume.
The eruption in Kīlauea's middle East Rift Zone started with a fissure eruption on January 3, 1983, and continued with few interruptions at Puʻu ʻŌʻō Cone, or temporarily from vents within a few kilometers to the east or west.
An eruption on the northeast flank of Puʻu ʻŌʻō on June 27, 2014, sent a lava flow to the northeast, where it eventually intersected and utilized old grounds cracks for part of its length. The flow exited the ground cracks in early September 2014 and approached the outskirts of the town of Pāhoa, where flows have persisted but have not reached critical infrastructure.
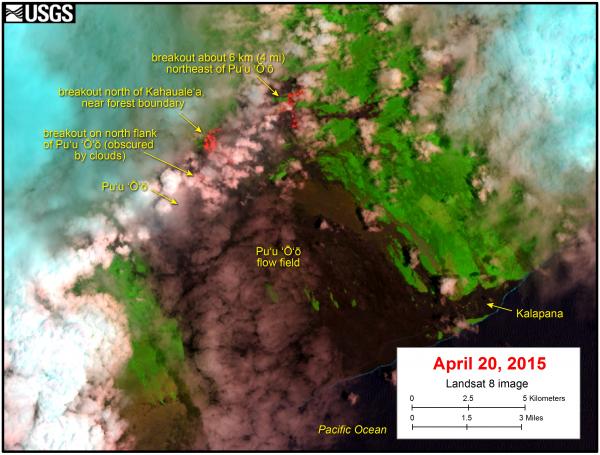
This satellite image was captured on Monday, April 20, 2015 by the Landsat 8 satellite. Although this is a false-color image, the color map has been chosen to mimic what the human eye would expect to see. Bright red pixels depict areas of very high temperatures and show active lava. White areas are clouds.
The lava flow field is partly obscured by clouds, but the image shows much of the activity on the June 27th flow. There have been three areas of breakouts active on the June 27th flow recently. The breakout on the north flank of Puʻu ʻŌʻō is obscured by clouds, but the breakout north of Kahaualeʻa is visible through patchy clouds in this image. This breakout has been active recently at the forest boundary, triggering small brush fires. The farthest breakout is about 6 km (4 miles) northeast of Puʻu ʻŌʻō, and consists of scattered activity at the forest boundary. Image credit: USGS
Hazard summary
East Rift Zone vents and flow field Lava flows from the June 27 breakout have advanced into Pāhoa and may threaten residential areas depending on their level of activity and advance rate. Near-vent areas could erupt or collapse without warning with spatter and/or ash being wafted within the gas plume. In addition, potentially-lethal concentrations of sulfur dioxide gas may be present within 1 km downwind of vent areas. Active lava flows within forested areas can produce methane blasts capable of propelling rocks and other debris into the air. All recently active lava flows are within Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park and adjacent State land managed by the Department of Land and Natural Resources or the Office of Hawaiian Affairs.
Kīlauea Crater Ash and Pele's hair can be carried several kilometers downwind, and potentially-lethal concentrations of sulfur dioxide can be present within 1 km downwind.
Source: HVO Kilauea Status issued Monday, April 27, 2015 7:15 AM HST (Monday, April 27, 2015 17:15 UTC).
Featured image credit: USGS/HVO

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules:
We reserve the right to remove any comments that violate these rules. By commenting on our website, you agree to abide by these guidelines. Thank you for helping to create a positive and welcoming environment for all.