NCEI scientists warn of weakening Atlantic Ocean currents, profound implications on global climate patterns
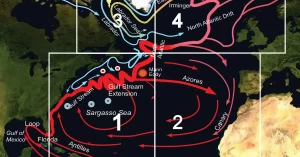
Scientists from the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) and the University of Maryland have provided evidence of a significant slowdown in the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a key climate regulator. Published in Frontiers in Marine Science, the research utilized over six decades of oceanic data to track the health of this vital oceanic component. This slowdown, observed primarily in the last two decades, could have profound implications on global climate patterns.