A continuous low-level eruption recorded at Cleveland volcano on Aleutian Islands

The current eruption of Cleveland Volcano, which began with an explosion on May 4, 2013, has transitioned into a continuous low-level eruption. The activity is characterized by long duration airwave signals measured on the nearby Okmok seismic network, 120 km (80 miles) to the northeast.
Satellite and webcam data suggest continuous low-level emissions of gas, steam, and minor amounts of ash over the past several hours with a faint plume extending eastward below 15,000 ft. Satellite data also show highly elevated surface temperatures at the summit.
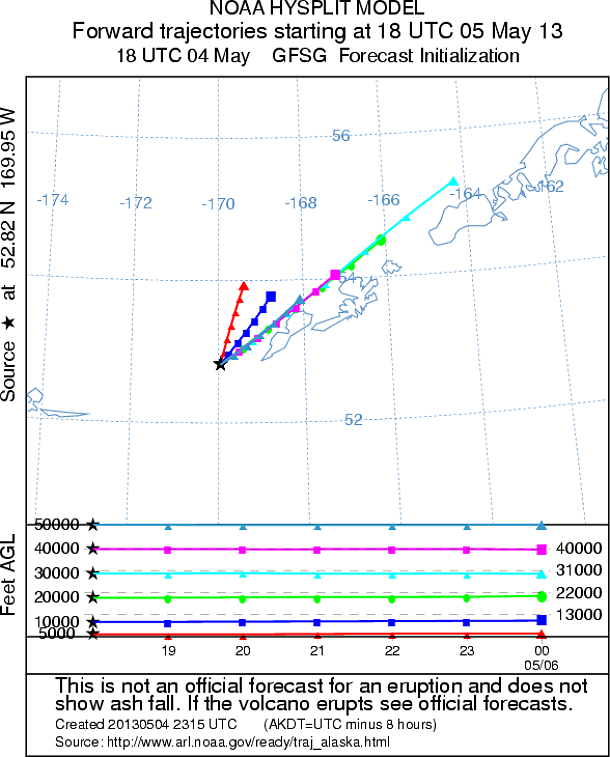
Mt. Cleveland 24 hours ash trajectory forecast (Credit: AVO/NOAA/ARL)
Sudden explosions of blocks and ash are possible with little or no warning. Ash clouds, if produced, could exceed 20,000 feet above sea level. If a large ash-producing event occurs, nearby seismic, infrasound, or volcanic lightning networks should alert AVO staff quickly. However, for some events, a delay of several hours is possible. Cleveland Volcano does not have a local seismic network and is monitored using only distant seismic and infrasound instruments and satellite data.
AVO will continue to monitor the volcano and issue additional information as available. On May 4, 2013 volcano alert level was raised from Advisory to Watch and aviation color code was changed from Yellow to Orange.
Source: AVO
Featured image: Small explosion at Cleveland volcano on July 20, 2007 (Credit: Photo courtesy of Doug Dasher, ADEC and Max Hoberg, School of Fisheries, UAF)

Commenting rules and guidelines
We value the thoughts and opinions of our readers and welcome healthy discussions on our website. In order to maintain a respectful and positive community, we ask that all commenters follow these rules.